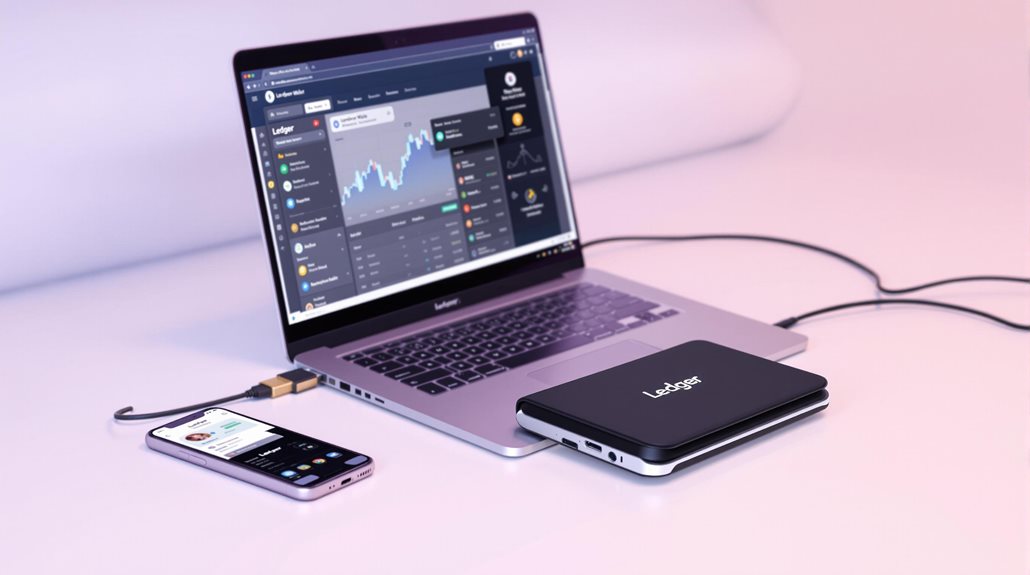
Getting a Bitcoin wallet starts with choosing between software or hardware options. Software wallets are free apps or programs that work on phones and computers, while hardware wallets are physical devices that store Bitcoin offline for extra security. Popular software choices include Exodus and Electrum, whereas Trezor and BitBox02 are well-known hardware options. The setup process typically involves downloading software or purchasing a device, then following the provider's security steps. There's much more to understand about wallet security and features.

Getting a Bitcoin wallet isn't as complicated as it might seem. When someone wants to store their Bitcoin, they have several wallet options to choose from. Each type of wallet serves different needs and comes with its own set of features. Proper identity verification is typically required during the setup process.
The most common types of Bitcoin wallets include software wallets, hardware wallets, paper wallets, brain wallets, and multi-signature wallets. Software wallets can be mobile apps, desktop programs, or web-based solutions. Hardware wallets are physical devices that keep Bitcoin offline, while paper wallets are simply printed versions of private keys and addresses. Brain wallets rely on memorized passphrases, though they're not recommended. Multi-signature wallets need multiple approvals before completing transactions. Users should consider implementing end-to-end encryption for any web-based wallet solutions. Unlike traditional wallets, crypto wallets use public keys to access funds stored on the blockchain.
When selecting a specific wallet, users typically look at reputable providers like Exodus, Electrum, or Trezor. These providers offer different features, and it's important to compare what each one offers. Some wallets support multiple cryptocurrencies, while others focus solely on Bitcoin. Users also need to check if the wallet works with their devices and operating systems. Hardware wallets like BitBox02 provide strong security protocols for enhanced protection.
The setup process involves either downloading wallet software or purchasing a hardware device. During setup, the wallet generates a recovery phrase that's vital for accessing funds if something goes wrong. Users store this phrase offline in multiple secure locations. Many wallets also include additional security features like PIN codes or passwords.
Security remains a top priority for Bitcoin wallet users. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of protection for online wallets. Regular software updates help protect against security vulnerabilities. Hardware wallet users only connect their devices to trusted computers or phones. Many people start with small transactions to test their new wallet's functionality.
Popular wallet providers regularly update their software and maintain active user communities. These communities often share experiences and provide feedback about wallet features and security. Open-source wallets offer transparency, letting users verify the code behind their wallet's operation.
The Bitcoin wallet market continues to evolve with new features and improvements. Providers compete to offer better security, easier interfaces, and more convenient ways to manage Bitcoin. Some wallets now include features like built-in exchanges or the ability to earn interest on stored Bitcoin.
As technology advances, wallet options expand, giving users more choices for how they want to store and manage their Bitcoin.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens if I Forget My Bitcoin Wallet Password?
If someone forgets their Bitcoin wallet password, they can't access their funds. There's no "forgot password" button or help desk to call.
The funds remain locked in the wallet forever unless they can remember or crack the password. Some people try password recovery services or special software to guess combinations.
It's estimated that around $140 million in Bitcoin is currently stuck in wallets with forgotten passwords.
Can Someone Steal My Bitcoin if They Hack My Phone?
Yes, hackers can potentially steal Bitcoin if they gain access to someone's phone. A compromised phone with a Bitcoin wallet is vulnerable to various attacks.
Malware can steal wallet data and private keys. Public Wi-Fi networks make phones susceptible to transaction interception.
Hackers might also use fake apps or phishing schemes to access wallet credentials. That's why many Bitcoin users keep large amounts in hardware wallets instead of phone-based wallets.
How Much Does It Cost to Maintain a Bitcoin Wallet?
The cost of maintaining a Bitcoin wallet varies by type.
Software and mobile wallets are typically free to use, while hardware wallets can cost between $50-$200 upfront.
There aren't many ongoing costs except for transaction fees, which usually range from $1.50 to $5 per transfer.
Some people choose custody services that charge annual fees of 0.5-2% of their holdings, but most wallet maintenance is free beyond the initial setup.
Can I Have Multiple Bitcoin Wallets Under One Identity?
Yes, it's possible to have multiple Bitcoin wallets under one identity.
There's no limit to how many wallets someone can create or own. People often maintain several wallets for different purposes, like keeping some Bitcoin for daily spending and others for long-term savings.
Each wallet functions independently but can be linked to the same person.
It's similar to having multiple bank accounts – they're separate but can belong to one individual.
Is My Bitcoin Wallet Information Visible to Government Authorities?
Bitcoin wallets operate on a public blockchain where anyone can see transaction records.
While wallet addresses aren't directly connected to real identities, government agencies can trace transactions using specialized tools.
When people use regulated exchanges that require ID verification, authorities can potentially link wallets to specific users.
The IRS, FBI, and other agencies work with blockchain analysis companies to monitor crypto movements and investigate suspicious activity.